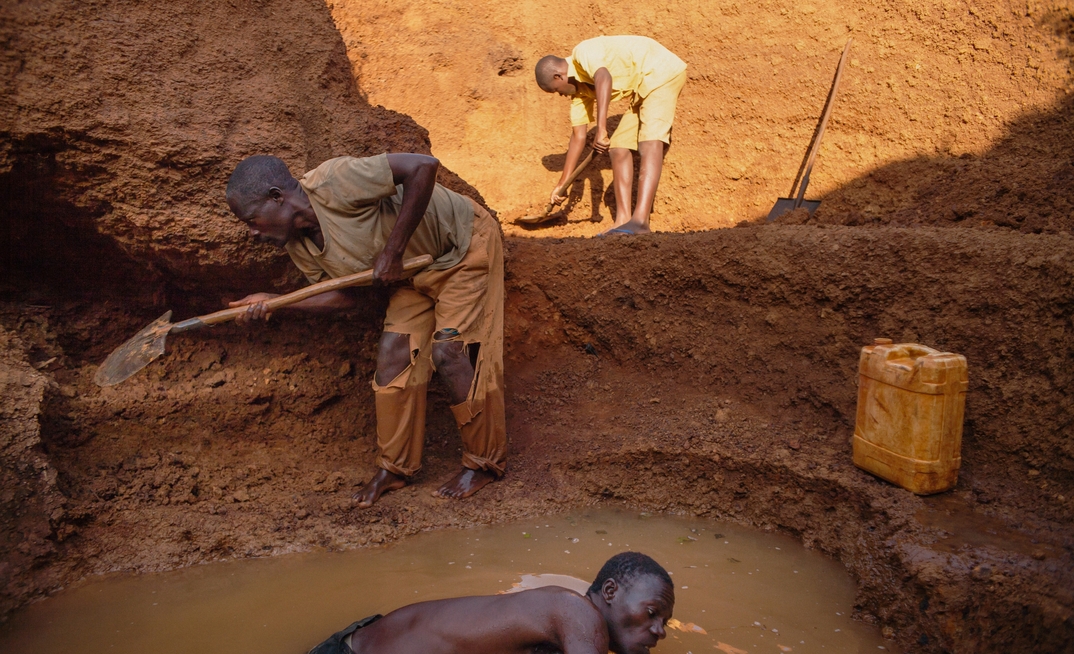
Africa is home to vast reserves of critical minerals essential for green technologies, such as electric vehicle batteries and wind turbines. As the global demand for clean energy surges, so will the need for African minerals.
A recent report by Zero Carbon Analytics highlighted the opportunity that this will present for the continent, which holds 30% of the global reserves of 'green' minerals.
The brief cited recent International Energy Agency (IEA) forecasts, which predict that within the next two decades, renewable energy technologies may drive up to 40% of the overall demand for copper and rare earth elements, between 60-70% of the total demand for nickel and cobalt, and nearly 90% of lithium demand.
Africa, which holds 92% of the world's platinum, 56% of cobalt, 54% of manganese, and 36% of chromium, is now at a crucial junction.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE
But realising the full potential of it's mineral wealth will be no easy feat. According to the report, strategic interventions and concerted efforts from governments, industry stakeholders, and regional bodies will be crucial.
Push for processing
Despite its abundant resources, Africa primarily exports raw minerals, missing out on the economic benefits of value addition. The continent accounts for a significant portion of global mineral reserves and production, yet much of the processing occurs abroad, primarily in China, which holds 85% of global processing capacity.
"Between 2005 and 2015, Chinese investment in the African mining industry grew 25 times," the report noted.
"China's control over mines in Africa has also been growing, reaching almost 7% of the total value of mines in 2018 in countries like Gabon, Ghana, South Africa, Zambia and Zimbabwe. Chinese firms control almost 41% of cobalt extraction in the DRC and nearly 28% of copper in the DRC and Zambia."
Increasing the continent's downstream processing capacity would not only result in higher-value products being exported but would also boost local industries and develop a more skilled workforce, according to the report.
Zero Carbon noted that several African countries are beginning to develop their mineral industries and limit the export of raw materials.
For instance, Ghana recently introduced a policy stating that lithium produced must be processed domestically before export.
But if the goal is to establish robust and well-developed mineral supply chains, regional cooperation will be key, according to Zero Carbon.
"Establishing all segments of a mineral supply chain within a single country is often not feasible due to a lack of economies of scale. For this reason, regional cooperation is key to achieving value addition of minerals in Africa," the brief stated.
Initiatives such as The African Green Minerals Strategy, established in 2024, and the Africa Continental Free Trade Agreement, established in 2021, are beginning to push for upstream value addition and increased economic integration.
Sustained regional collaboration efforts will be key to ensuring that resource-rich countries receive adequate pay-out, Zero Carbon wrote.
Data & skills gaps
While improved downstream capacities may elevate Africa's position in the global mineral supply chain, more exploration remains key, according to the brief.
In 2022, the continent accounted for 10% of global exploration spending, signifying that much of its wealth remains undetected. Increased geological mapping would not only unveil reserves but also improve the environmental feasibility of mining projects.
Skills gaps and poor infrastructure also pose a challenge to the industry. Inadequate transport and energy networks increase operational costs and hamper competitiveness, the report noted.
Addressing these challenges could be crucial to attracting investors, which would, in turn, boost the mining industry.
Flailing tax revenues
Zero Carbon's report noted that many Sub-Saharan African nations, despite their mineral wealth, struggle with limited tax revenues from the mining sector.
While some countries have implemented royalties and corporation taxes, revenue remains restricted due to low tax rates aimed at attracting investment.
This strategy has led to regional competition to offer the lowest tax burden, hindering revenue generation. Cooperation again emerges as a solution to this issue, as better collaboration could lead to more cohesive and beneficial tax policies.
"Pan-African cooperation is key to prevent such tax dumping," the report noted.
"The International Monetary Fund estimates that African countries are losing between US$450 million and US$730 million per year in corporate income tax on average from tax avoidance by multinational enterprises. Some countries have already taken steps to address tax vulnerabilities in the mining sector. South Africa and Nigeria have imposed restrictions on interest deductions, while Sierra Leone has stopped negotiating fiscal terms on a mine-by-mine basis."
Africa's mineral resources hold immense potential for sustainable development, particularly in the context of the global shift towards renewable energy. But unlocking this potential requires concerted efforts to promote value addition, attract investment, and address environmental and governance challenges. At the centre of these efforts is better regional coordination, which according to Zero Carbon, can help the continent climb ranks in the global value chain.